Models
IDE Model Introduction
Models are the core components that drive agent behavior, determining the boundaries of capabilities in code understanding, generation, reasoning, and tool calling. Based on deployment and management methods, models can be divided into two main categories:
Agent Hub Models: Pre-configured agents hosted on the official Agent Hub, maintained by the official team and ready to use out-of-the-box. These models are automatically integrated through account authorization without local key management, suitable for quickly enabling standardized capabilities.
Local Custom Models: Models explicitly defined through project-level
config.yamlfiles, supporting private deployments, mixed providers, and fine-grained control over roles, capabilities, context strategies, and HTTP request behaviors. Suitable for scenarios with higher requirements for security, performance, or customization.
Regardless of the approach used, both provide a unified abstraction layer, ensuring consistent, composable, and auditable model behavior across modes such as Chat, Edit, Autocomplete, and Agent.
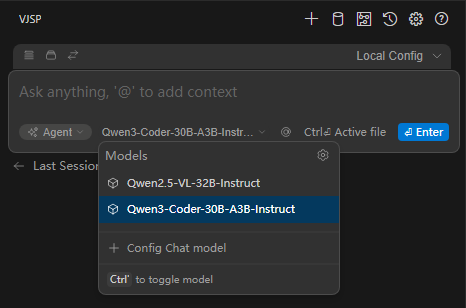
Local Models
Introduction
Agents are defined through the config.yaml specification.
Agents consist of models, rules, and tools (MCP servers).
📄 Configuring Models, Rules & Tools
Learn how to use the configuration system, including using Hub models, rules & tools, creating local configurations, and organizing configuration structures.
🤖 Understanding Config Files
Learn how to build and configure config files, understand their functions, and customize them according to your development workflow.
Creating Local Models
Select Local Agent, click the settings button next to it to open the config.yaml file of the locally configured agent page.
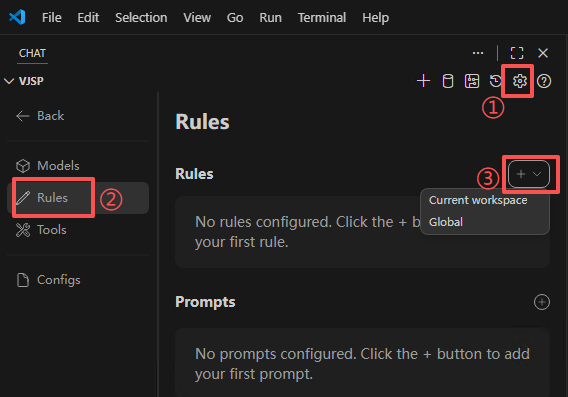
Set model information in the file and save.
Configuration Properties
Below are details of each property that can be set in config.yaml.
All properties at all levels are optional unless explicitly marked as "Required".
name(Required)version(Required)schema(Required)modelscontextrulespromptsdocsmcpServersdata
name
The name property is used to specify the name of the project or configuration file.
version
The version property is used to specify the version of the project or configuration file.
schema
The schema property is used to specify the schema version used by config.yaml, such as v1.
models
The models section is used to define the language models used in the configuration, which can be used for functions such as chat, editing, and summarizing.
Property Description:
name(Required): Unique name used to identify the model in the configuration.provider(Required): Model provider (e.g.,vjsp).model(Required): Specific model name.apiBase: Can be used to override the model's default API base URL.roles: Array type, specifies the roles the model can assume, includingchat(conversation),autocomplete(autocomplete),embed(embedding),rerank(reranking),edit(editing),apply(execution),summarize(summarization). Default value is[chat, edit, apply, summarize]. Note that thesummarizerole is currently not enabled.capabilities: String array, used to represent model capabilities, overrides automatically detected capabilities based on provider and model. For detailed information, refer to the Model Capabilities Guide. Supported capabilities include:tool_use: Enable function/tool call support (required for Agent mode)image_input: Enable image upload and processing support
These capabilities are automatically detected for most models, but can be manually overridden when using custom deployments or when automatic detection fails.
vjsp-api-key
The secret key provided by the model service provider. Please store it securely.
Model YAML Configuration Example
name: TestCaseGenerator
version: 1.0.0
schema: v1
# Basic model information
models:
- name: Qwen3
provider: openai
model: Qwen3
apiBase: https://XXXX.XXX.cn/v1
capabilities:
- tool_use
roles:
- chat
- edit
- apply
requestOptions:
headers:
vjsp-api-key: b4XXXXXXXXXX